AWS-Cloud Multi-Region Network Architecture¶
1. Web-Application Architecture¶
Secure and scalable cloud applications on AWS with the essential building blocks that form a typical AWS end-to-end application architecture.
2. Analytics-Application Architecture¶
Create a Network Architecture tailored to your application's specific needs.
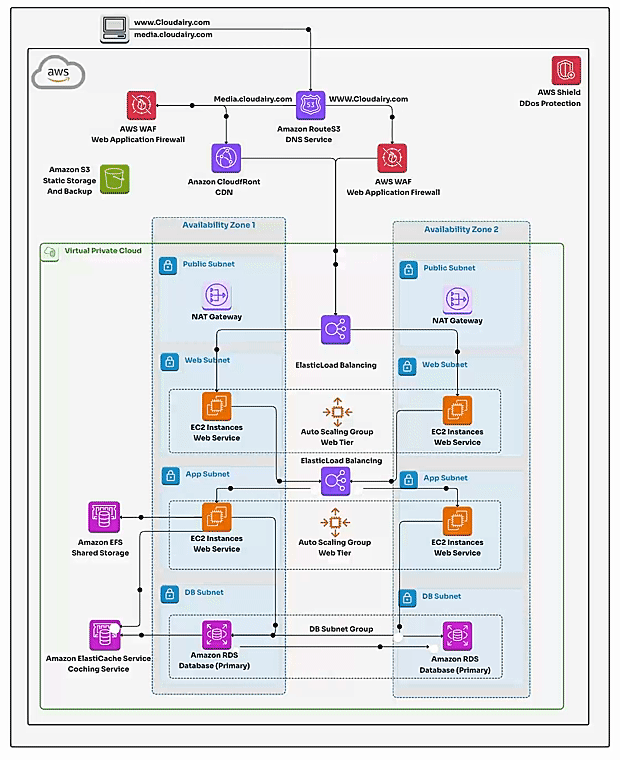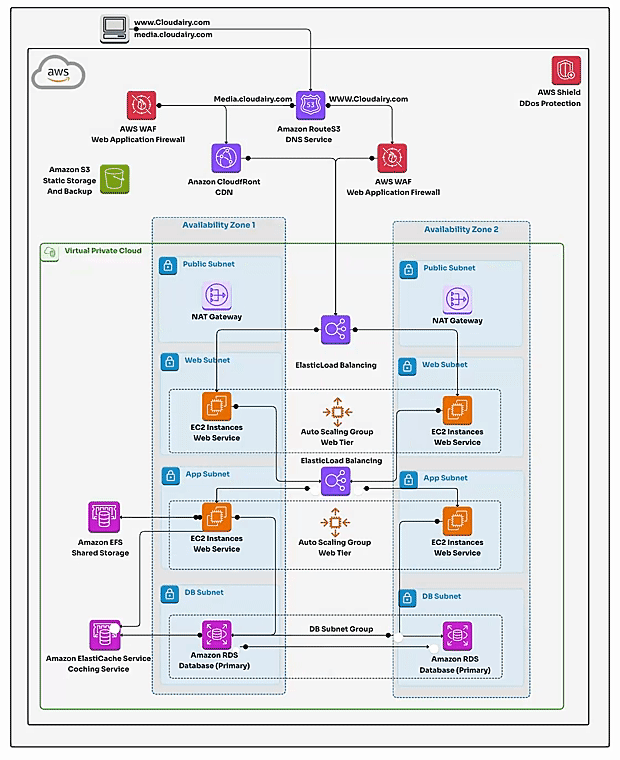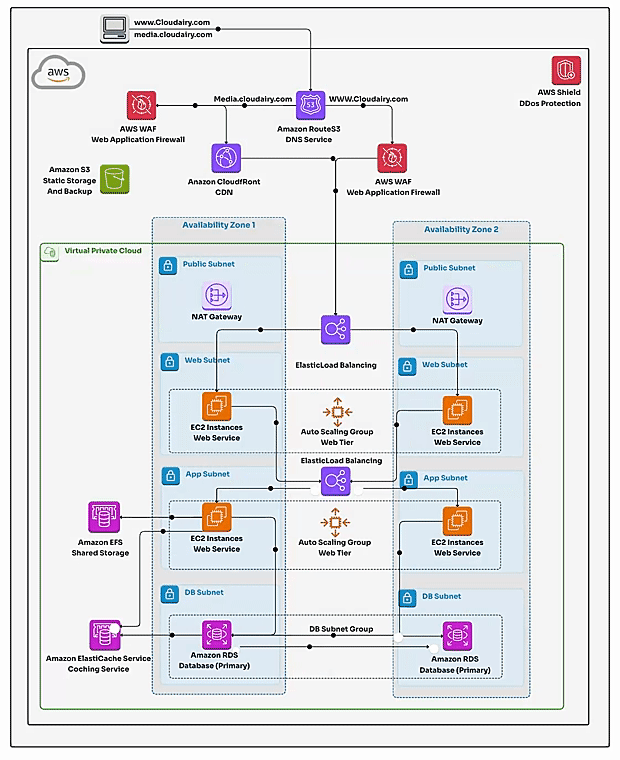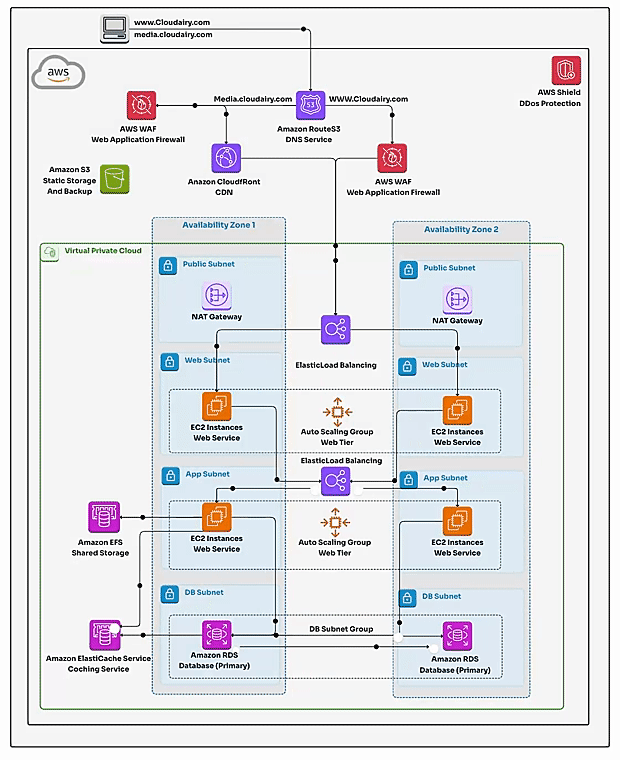
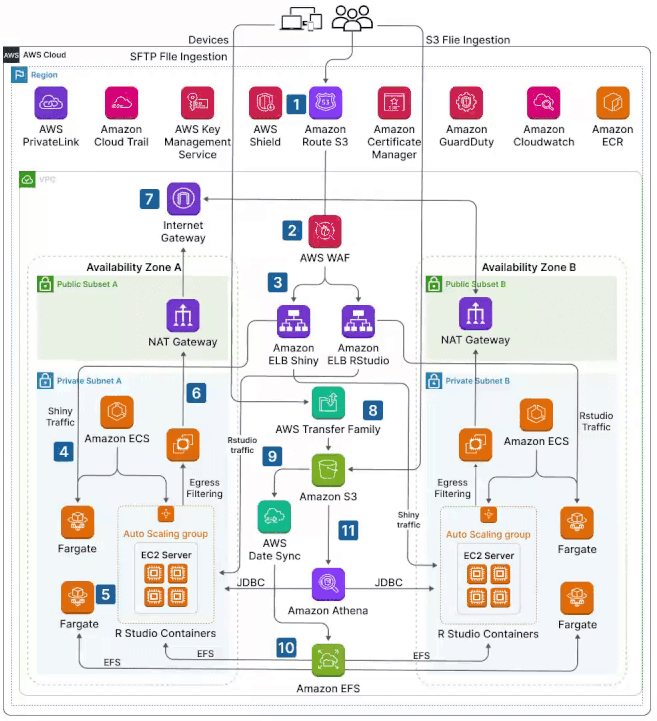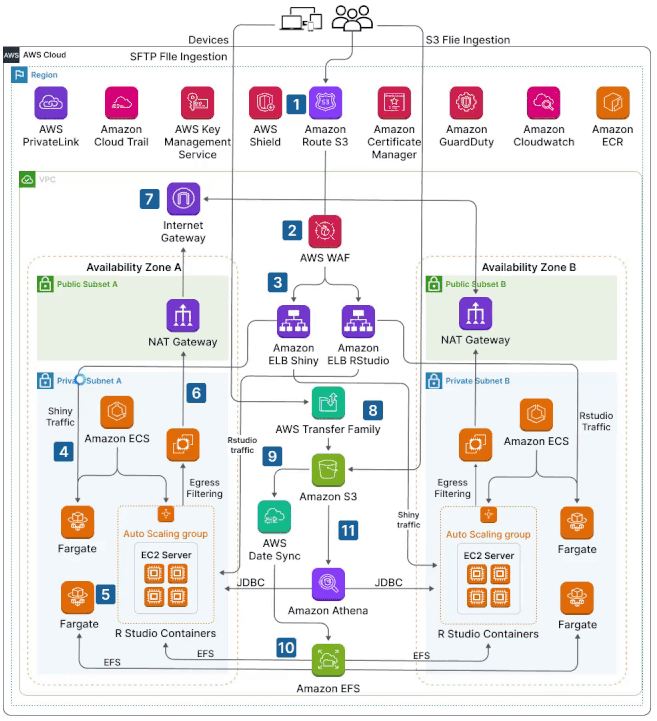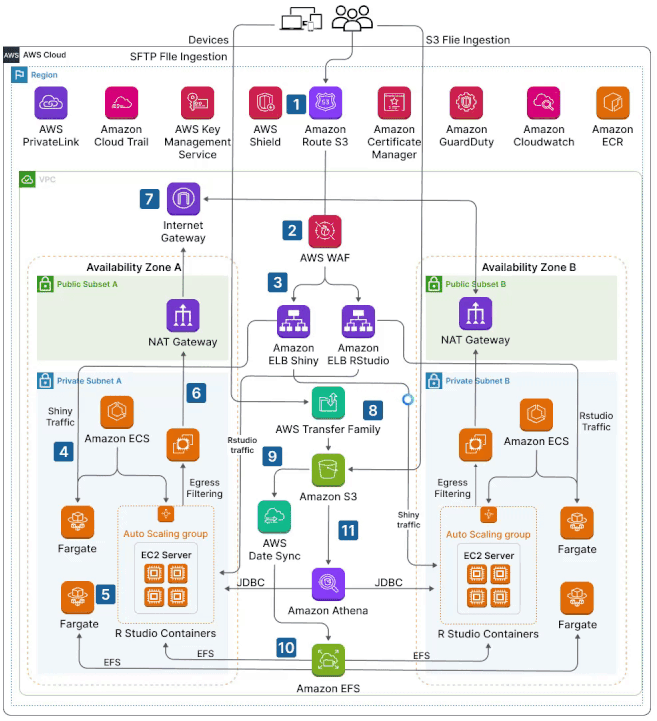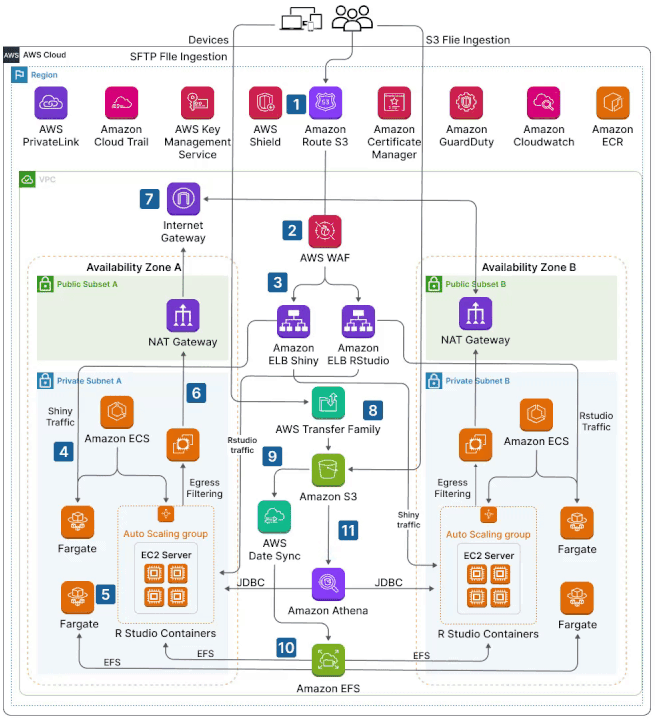
- 1. Route 53: This is your domain name manager in the cloud. Route 53 directs users to your application's endpoint (often a Load Balancer) and allows you to register and manage your domain names. Also, CloudFront expedite content delivery seamlessly.
- 2.
AWS WAF - 3. Elastic Load Balancing (ELB): ELB distributes incoming application traffic across multiple instances for better availability and fault tolerance.
-
4. ✅Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): The foundation of AWS network architecture is the VPC. It's a logically secure and isolated seprivate network of the AWS cloud where you can separatedly launch resources in a virtual network that you define. VPC enables you to control IP address ranges, subnets, route tables, security groups, and network gateways.
- ✅Subnets: Within a VPC, you create subnets to segment the IP address range as subdivisions within your VP. Subnets can be public (accessible from the Internet) or private (not accessible from the Internet). They help organize and control network traffic flow and isolate public-facing components from private ones.
- ✅Route Tables: Route tables define how traffic is routed between subnets and to external networks. They determine the paths that network traffic takes within the VPC.
- ✅Security Groups: Security groups act as virtual firewalls for instances. They control inbound and outbound traffic based on rules you define. Each instance can be associated with one or more security groups.
- Security Groups and Network ACLs: Implement granular security controls on the subnet and instance levels.
- ✅Internet Gateway: The Internet Gateway enables communication between instances in your VPC and the public internet. It's required for resources in public subnets to access the internet.
- Internet & NAT Gateways: To protect your resources, make sure you have a secure connection to the internet and efficiently handle outgoing traffic.
- ✅VPC Peering: VPC peering allows you to connect multiple VPCs together, enabling direct communication between them. Peered VPCs can route traffic between them as if they were part of the same network.
- ✅Transit Gateway: The Transit Gateway simplifies network architecture by allowing centralized connectivity for multiple VPCs and on-premises networks. It reduces the complexity of managing point-to-point connections.
- ✅AWS PrivateLink: As discussed earlier, AWS PrivateLink provides private connectivity between VPCs, supported AWS services, and your on-premises networks without exposing traffic to the public internet.
-
5.
- 6.
✔️
✔️
✔️ **Servers**: The workhorses of your application. Web servers handle requests, application servers handle the logic. Run them on EC2 instances (flexible, separate, or combined).
✔️ **RDS**: This manages service stores your application's data. It offers a variety of database engine options and ensures reliability and scalability.
✔️ **Load Balancer**: It distributes incoming user requests across multiple EC2 instances, ensuring your application remains available and performs fine under heavy traffic.
✔️ **Auto Scaling Group**: An Auto Scaling Group scales your EC2 instances up or down based on predefined rules, ensuring your application can handle fluctuating loads with ease.
✔️ **Security Groups**: These are virtual firewalls for your EC2 instances. They control incoming and outgoing traffic, enforcing security and access restrictions.
✔️
3. Overall Network Architecture¶
-
Amazon Availability Zones & Regions: For fault tolerance and high availability, utilize many AZs and regions.
-
AWS Transit Gateway: Use a centralized hub to streamline network communication between VPCs and on-premises networks.
-
Direct Connect/VPN: Create safe links between your AWS environment and data centers located on-site.
-
Transit Gateway & VPC Peering Peering: Enable smooth data flow by facilitating connectivity across regions.